Neural Network Explained Simply: How Machines Learn Like the Human Brain
Neural network power everything from voice assistants to self-driving cars, yet they are often described in ways that feel unnecessarily complex. We are going to explain neural networks simply, breaking down how they work, why they matter, and how they learn—without heavy math or jargon. By the end, you will understand neural networks well enough to explain them to someone else with confidence.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Neural Network?
- Why Neural Networks Exist
- How Neural Networks Work Step by Step
- Common Types of Neural Networks
- Real-World Applications of Neural Networks
- Strengths and Limitations
- The Future of Neural Networks
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
What Is a Neural Network?
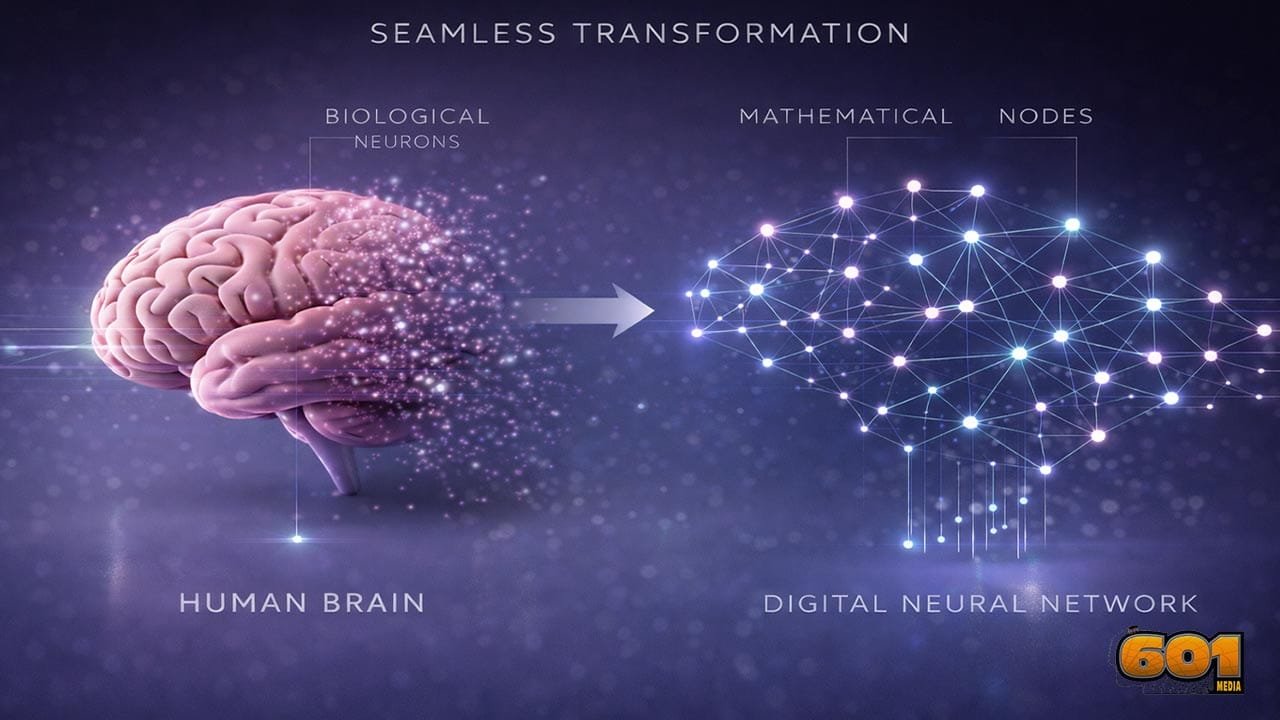
A neural network is a computer system designed to recognize patterns by learning from data. It is inspired by the human brain, which processes information using interconnected neurons. Instead of biological neurons, neural networks use mathematical nodes that work together to make decisions. At its core, a neural network answers one simple question repeatedly: given this input, what output is most likely correct? Over time, it gets better at answering that question by learning from mistakes.
Why Neural Networks Exist
Traditional computer programs rely on fixed rules written by humans. That approach works well for structured problems like accounting or scheduling. But many real-world problems—such as recognizing faces or understanding speech—do not have clear rules. Neural networks exist because some problems are easier to learn from examples than to define with logic. Instead of programming every rule, engineers provide data and let the system learn patterns on its own. This shift from rule-based programming to learning-based systems is one of the most important developments in modern technology.
How Neural Networks Work Step by Step
Neural networks operate through layers of connected nodes. Each layer plays a specific role in transforming raw data into useful predictions. First, data enters the input layer. This could be pixels in an image, words in a sentence, or numbers from sensors. Each input is passed to the next layer with a weight that represents importance. Second, the hidden layers process the data. Each node multiplies inputs by weights, adds a bias, and applies an activation function. This step determines whether information should pass forward. Third, the output layer produces a final result, such as identifying an object or predicting a value. Learning happens through a process called training. The network compares its prediction to the correct answer, calculates the error, and adjusts its weights to reduce future mistakes. Repeating this cycle thousands or millions of times allows the network to improve.
Common Types of Neural Networks
Different problems require different neural network designs. Feedforward neural networks are the simplest form. Information moves in one direction, from input to output. These are often used for basic prediction tasks. Convolutional neural networks specialize in visual data. They detect edges, shapes, and patterns, making them ideal for image recognition and medical imaging. Recurrent neural networks handle sequences and time-based data. They are useful for language translation, speech recognition, and financial forecasting. Each type exists because real-world data behaves differently depending on context and structure.
Real-World Applications of Neural Networks
Neural networks are deeply embedded in everyday technology. Smartphones use them for facial recognition and voice commands. Streaming platforms rely on them to recommend content. Banks use them to detect fraud by identifying unusual behavior patterns. In healthcare, neural networks assist doctors by analyzing medical images and predicting disease risks. In transportation, they help vehicles understand their surroundings and make driving decisions. These systems succeed because neural networks excel at processing massive amounts of data faster and more consistently than humans.
Strengths and Limitations
The greatest strength of neural networks is adaptability. Once trained, they can handle complex, noisy, and unstructured data with impressive accuracy. However, they also have limitations. Neural networks require large datasets, significant computing power, and careful tuning. They can also behave like black boxes, making it difficult to explain how they reach certain conclusions. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for responsible and effective use.
The Future of Neural Networks
Neural networks continue to evolve rapidly. Advances in hardware, data availability, and learning techniques are making them more efficient and interpretable. Future systems will likely require less data, learn faster, and explain their decisions more clearly. As these improvements mature, neural networks will expand into areas such as personalized medicine, climate modeling, and scientific discovery. Their role will not be to replace humans, but to amplify human decision-making at scale.
Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
Neural networks are powerful because they shift computing from rigid rules to flexible learning. By understanding neural networks simply, you gain insight into the foundation of modern AI systems shaping business, science, and daily life. The most important takeaway is this: neural networks do not replace human intelligence—they extend it by uncovering patterns we could never process alone.
Resources
- Goodfellow, Bengio, Courville – Deep Learning (MIT Press)
- Stanford CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks
- MIT OpenCourseWare – Introduction to Neural Networks
- IBM AI Education Resources
I am a huge enthusiast for Computers, AI, SEO-SEM, VFX, and Digital Audio-Graphics-Video. I’m a digital entrepreneur since 1992. Articles include AI researched information. Always Keep Learning! Notice: All content is published for educational and entertainment purposes only. NOT LIFE, HEALTH, SURVIVAL, FINANCIAL, BUSINESS, LEGAL OR ANY OTHER ADVICE. Learn more about Mark Mayo