Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid: Which Strategy Wins?
Modern enterprises are no longer asking whether to adopt cloud computing, but how to structure it for long-term advantage. As digital transformation accelerates, two dominant approaches continue to shape enterprise IT strategy: multi-cloud and hybrid cloud. While both promise flexibility, resilience, and scalability, their strategic implications differ significantly. This article breaks down the real-world differences, strengths, risks, and decision factors to determine which strategy truly wins.
Table of Contents
- What Is Multi-Cloud?
- What Is Hybrid Cloud?
- Strategic Drivers Behind Each Model
- Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid: Core Differences
- Security, Compliance, and Risk
- Cost, Performance, and Operations
- Industry Use Cases
- How to Choose the Right Strategy
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
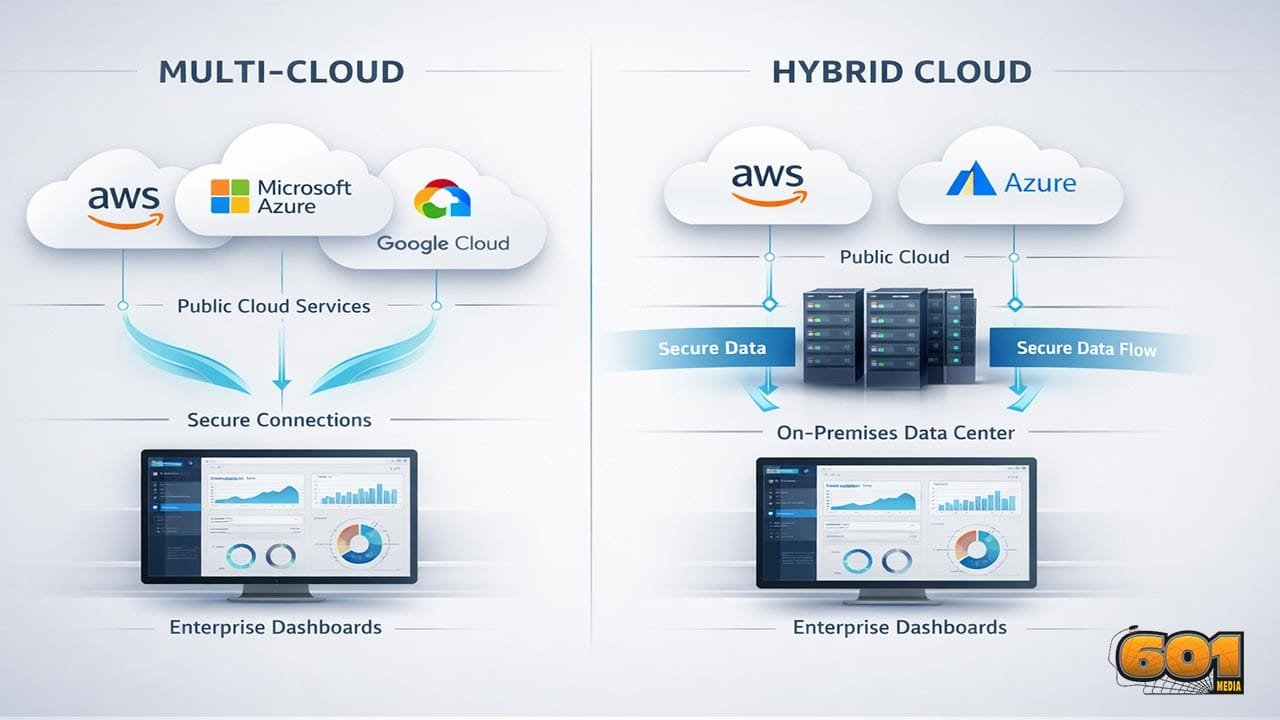
What Is Multi-Cloud?
Multi-cloud refers to the use of two or more public cloud providers within a single organization. These providers operate independently, and workloads are distributed across them based on performance, geographic reach, cost optimization, or specialized services. A common example includes using AWS for compute-heavy workloads, Microsoft Azure for enterprise productivity integration, and Google Cloud for advanced analytics and machine learning. The defining characteristic of multi-cloud is optionality. Organizations deliberately avoid dependence on a single vendor. According to Flexera’s 2024 State of the Cloud Report, over 87% of enterprises now operate in a multi-cloud environment, driven primarily by risk mitigation and service specialization.
What Is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure, private cloud environments, and public cloud services into a unified architecture. The key differentiator is integration. Data and workloads move seamlessly between environments based on security, latency, or regulatory needs. Hybrid cloud is often favored by organizations with legacy systems, strict compliance requirements, or predictable workloads that benefit from private infrastructure while still leveraging public cloud elasticity. Gartner projects that by 2027, over 70% of enterprises will adopt hybrid cloud as their primary operating model due to regulatory pressure and data sovereignty concerns.
Strategic Drivers Behind Each Model
Multi-cloud is driven by strategic flexibility. Enterprises seek leverage in vendor negotiations, protection against outages, and access to best-of-breed services. It is a competitive strategy as much as a technical one. Hybrid cloud is driven by control and continuity. Organizations with mission-critical systems, sensitive data, or capital-intensive infrastructure investments use hybrid cloud to modernize without disruption. In short, multi-cloud optimizes choice, while hybrid cloud optimizes control.
Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid: Core Differences
Multi-cloud environments are horizontally distributed across vendors, while hybrid cloud environments are vertically integrated across environments. Multi-cloud complexity emerges from tooling fragmentation and governance sprawl. Hybrid cloud complexity stems from orchestration and interoperability challenges. From an architectural perspective, multi-cloud emphasizes portability. Hybrid cloud emphasizes integration.
Security, Compliance, and Risk
Hybrid cloud offers superior control over sensitive workloads. Data residency, encryption standards, and access controls can be tightly governed on-premises while bursting into public cloud when needed. Multi-cloud improves resilience by reducing single points of failure. However, it introduces policy inconsistency risk if identity management and security posture are not unified. IBM research indicates that organizations with fragmented cloud security tools experience 30% higher breach costs than those with centralized governance models.
Cost, Performance, and Operations
Multi-cloud enables cost arbitrage by shifting workloads to the most economical provider. However, operational overhead is higher due to duplicated skills, contracts, and monitoring systems. Hybrid cloud often delivers predictable costs for steady workloads while using public cloud elasticity for spikes. Performance benefits arise from low-latency access to on-prem systems. FinOps maturity is critical in both models. Without cost governance, cloud sprawl erodes ROI regardless of strategy.
Industry Use Cases
Financial services favor hybrid cloud to meet regulatory compliance while leveraging cloud analytics. Media and gaming companies adopt multi-cloud to optimize global content delivery and reduce latency. Healthcare organizations use hybrid cloud to protect patient data while enabling AI-driven diagnostics in the public cloud. No single model dominates across industries. Context determines superiority.
How to Choose the Right Strategy
Choose multi-cloud if vendor independence, geographic redundancy, and service specialization are strategic priorities. Choose hybrid cloud if regulatory compliance, legacy system integration, and data control are non-negotiable. Leading enterprises increasingly blend both approaches, creating hybrid multi-cloud architectures that maximize resilience and flexibility. The winning strategy is alignment, not architecture.
Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
Multi-cloud does not defeat hybrid cloud, and hybrid cloud does not eliminate the value of multi-cloud. The real winner is strategic clarity. Organizations that align cloud architecture with business objectives, regulatory realities, and operational maturity consistently outperform those chasing trends. In the next decade, success will belong to enterprises that design cloud strategies as dynamic systems, not static decisions.
I am a huge enthusiast for Computers, AI, SEO-SEM, VFX, and Digital Audio-Graphics-Video. I’m a digital entrepreneur since 1992. Articles include AI researched information. Always Keep Learning! Notice: All content is published for educational and entertainment purposes only. NOT LIFE, HEALTH, SURVIVAL, FINANCIAL, BUSINESS, LEGAL OR ANY OTHER ADVICE. Learn more about Mark Mayo