Serverless Architecture — What It Is & How It Works
Serverless architecture is a cloud-native approach that removes the need for developers to manage servers, enabling faster development, automatic scaling, and cost-efficient execution. Instead of provisioning infrastructure, teams focus entirely on writing business logic while cloud providers handle execution, availability, and scaling behind the scenes.
Table of Contents
- What Is Serverless Architecture?
- How Serverless Architecture Works
- Key Components of Serverless Architecture
- Benefits of Serverless Architecture
- Challenges and Limitations
- Common Serverless Use Cases
- Serverless vs Traditional Architecture
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
What Is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless architecture is a cloud computing execution model where the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation and provisioning of servers. Despite the name, servers still exist, but developers never interact with them directly. In a serverless model, applications are broken into discrete, event-driven functions that execute only when triggered. Billing is based on actual execution time rather than pre-allocated capacity, making serverless particularly attractive for variable or unpredictable workloads.
How Serverless Architecture Works
Serverless systems operate on an event-driven basis. Events such as HTTP requests, database updates, file uploads, or message queue activity trigger functions to execute. When an event occurs, the cloud provider automatically spins up the required runtime environment, executes the function, and shuts it down once execution completes. This process happens in milliseconds and scales transparently, even under massive traffic spikes. From an innovation management perspective, this model reduces operational friction and accelerates experimentation by shortening the path from idea to deployment.
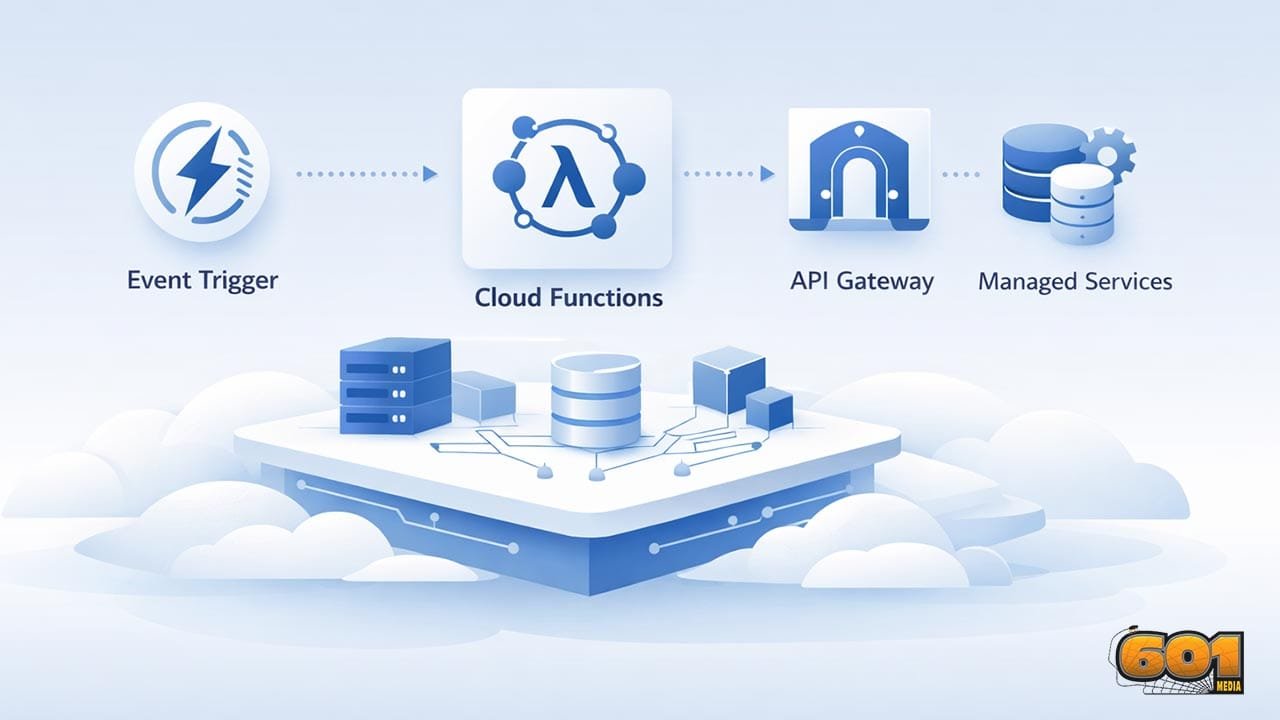
Key Components of Serverless Architecture
Function as a Service (FaaS) is the core building block, allowing developers to deploy individual functions without managing infrastructure. Backend as a Service (BaaS) components such as managed databases, authentication services, and storage replace traditionally self-hosted systems. API gateways act as entry points, routing requests to appropriate functions while handling security, throttling, and monitoring. Event sources such as message queues, cron jobs, or object storage changes drive execution and enable loose coupling between services.
Benefits of Serverless Architecture
Serverless significantly reduces operational overhead by eliminating server provisioning, patching, and capacity planning. Automatic scaling ensures applications handle traffic spikes without manual intervention, improving resilience and customer experience. Cost efficiency is achieved through pay-per-execution pricing, which research from cloud providers shows can reduce infrastructure costs by 30–70% for burst-driven workloads. Development velocity improves as teams focus on business logic rather than infrastructure, enabling faster product iterations and continuous innovation.
Challenges and Limitations
Cold start latency can occur when functions are invoked after periods of inactivity, which may impact real-time applications. Vendor lock-in is a strategic concern, as serverless implementations often rely on provider-specific services and APIs. Observability and debugging can be more complex due to distributed execution and ephemeral environments. Not all workloads are suitable; long-running processes and latency-sensitive systems may require hybrid or container-based architectures.
Common Serverless Use Cases
RESTful APIs and microservices benefit from serverless due to modularity and independent scaling. Data processing pipelines leverage event-driven execution for real-time analytics and ETL tasks. IoT backends use serverless to process device telemetry efficiently at scale. Scheduled jobs and automation workflows eliminate the need for always-on servers.
Serverless vs Traditional Architecture
Traditional architectures require pre-provisioned servers, manual scaling, and ongoing maintenance. Serverless shifts responsibility to the cloud provider, offering elasticity and reduced total cost of ownership. From a technology management standpoint, serverless aligns strongly with agile, lean, and experimentation-driven operating models.
Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
Serverless architecture represents a fundamental shift in how modern applications are designed, built, and operated. By abstracting infrastructure complexity, organizations unlock faster innovation cycles, lower operational risk, and improved scalability. The most important takeaway is strategic fit: serverless delivers maximum value when aligned with event-driven, modular, and rapidly evolving digital products.
Resources
- AWS Serverless Architecture Whitepaper
- Google Cloud Serverless Overview
- Microsoft Azure Serverless Documentation
- CNCF Serverless Landscape
I am a huge enthusiast for Computers, AI, SEO-SEM, VFX, and Digital Audio-Graphics-Video. I’m a digital entrepreneur since 1992. Articles include AI researched information. Always Keep Learning! Notice: All content is published for educational and entertainment purposes only. NOT LIFE, HEALTH, SURVIVAL, FINANCIAL, BUSINESS, LEGAL OR ANY OTHER ADVICE. Learn more about Mark Mayo